Spanning Multiple Cells
Widgets can take up more than a single cell in the grid; to do this, we'll use
the columnspan and rowspan options when gridding the widget. These are
analogous to the "colspan" and "rowspan" attribute of HTML tables.
Here is an example of creating a user interface with multiple widgets, some that take up more than a single cell.
| Gridding multiple widgets |
|---|
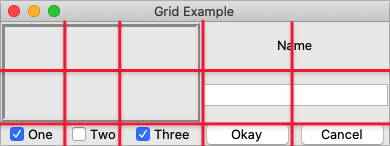 |
/// cargo run --example spanning_multiple_cells use tk::*; use tk::cmd::*; fn main() -> TkResult<()> { let tk = make_tk!()?; let root = tk.root(); let c = root.add_ttk_frame( "c" )?; c.add_ttk_frame( "f" -borderwidth(5) -relief("ridge") -width(200) -height(100) )?; c.add_ttk_label( "namelbl" -text("Name") )?; c.add_ttk_entry( "name" )?; c.add_ttk_checkbutton( "one" -text("One") -variable("one") -onvalue(1) )?; tk.set( "one" , 1 ); c.add_ttk_checkbutton( "two" -text("Two") -variable("two") -onvalue(1) )?; tk.set( "two" , 0 ); c.add_ttk_checkbutton( "three" -text("Three") -variable("three") -onvalue(1) )?; tk.set( "three", 1 ); c.add_ttk_button( "ok" -text("Okay") )?; c.add_ttk_button( "cancel" -text("Cancel") )?; tk.grid( ".c" -column(0) -row(0) )?; tk.grid( ".c.f" -column(0) -row(0) -columnspan(3) -rowspan(2) )?; tk.grid( ".c.namelbl" -column(3) -row(0) -columnspan(2) )?; tk.grid( ".c.name" -column(3) -row(1) -columnspan(2) )?; tk.grid( ".c.one" -column(0) -row(3) )?; tk.grid( ".c.two" -column(1) -row(3) )?; tk.grid( ".c.three" -column(2) -row(3) )?; tk.grid( ".c.ok" -column(3) -row(3) )?; tk.grid( ".c.cancel" -column(4) -row(3) )?; Ok( main_loop() ) }